Cutting pliers are indispensable in the world of tools and come in a wide variety of shapes and designs. They are used for numerous applications in many areas. Whether wire processing, cutting cables, bolts, nails, cable ties or electronic components - cutting pliers are everywhere. In this blog post, we take a detailed look at the different types of cutting pliers and the different shapes of their cutting edges.
Types of cutting pliers
Cutting edge in a perpendicular position:
These pliers, such as end cutting nippers, carpenters' pincers, concreters' nippers and lever end cutting nippers, are ideal for situations where access to the material to be cut is only possible from the front or a flush cut is required. Their design enables efficient working, especially when lateral space is limited.
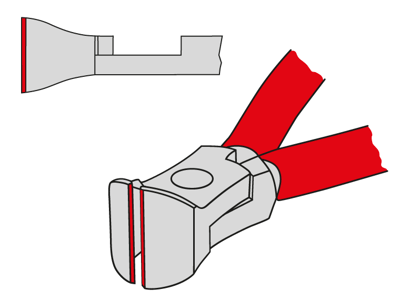

Cutting edges in an oblique position:
Oblique cutters are specialised pliers that are used in situations where neither frontal nor lateral access to the material is possible. Although they are used less frequently than other types, they are still irreplaceable in certain scenarios.
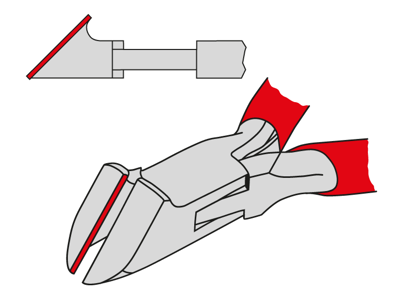

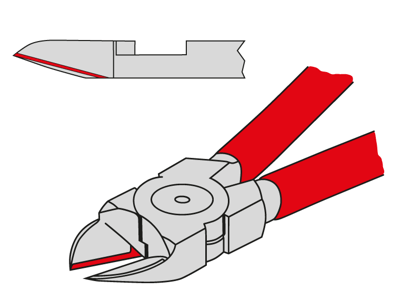
Cutting edge in a parallel position:
Side cutting edge: These pliers are the most widely used cutting pliers and are available in various lengths and for a wide range of materials. Examples include diagonal cutters, combination pliers, radio pliers, stork beak pliers, electricians' pliers and flat nose pliers with cutting edge.

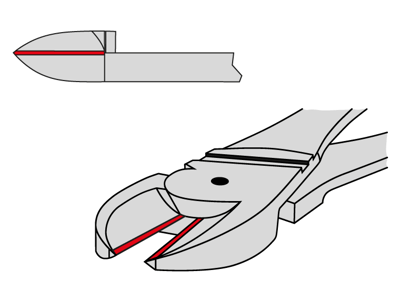
Centre cutting edge: Centre cutters offer high cutting edge stability with a favourable wedge angle and are particularly robust. Examples are centre cutters or bolt cutters.

Shapes of the cutting edge
Different cutting edge shapes play a decisive role in effectively cutting through different materials. Here are some important shapes:
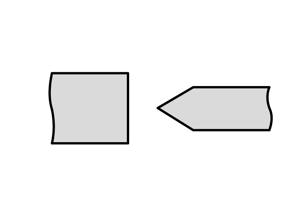
- Bite cut with outer bevel: This shape, with bevelled cutting edges, reduces the load on the blade and is suitable for a wide range of materials.
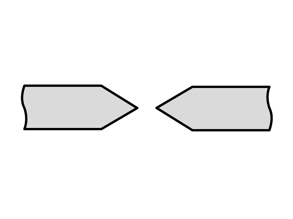

- Bite cut without outer bevel: Suitable for soft materials such as copper or plastics, this shape enables flush cuts.

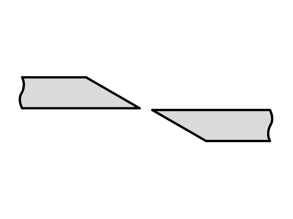
- Knife or anvil cut: This cut is ideal for fibre bundles such as ropes and cords, for example, but also for soft materials such as rubber, wood and plastics. Aluminium or copper can also be cut through in small diameters.

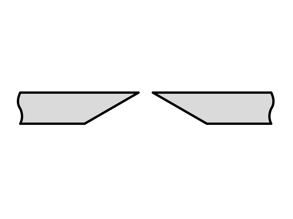
- Shear cut: This shape is used for various shears and produces the lowest cutting forces, especially for cable and wire ropes as well as sheet metal.

Conclusion
Cutting pliers are versatile tools that enable a wide range of applications thanks to their different types and cutting shapes. By making the right choice, you can increase the efficiency of your work processes and achieve precise results.
Products mentioned: 99 14 300 High Leverage Concreters' Nipper - 62 12 120 Electronics Oblique Cutting Nipper - 70 06 160 Diagonal Cutter - 71 72 910 Bolt Cutter - 71 01 160 KNIPEX CoBolt® S Compact Bolt Cutters - 78 03 125 ESD Electronic Super Knips® ESD - 94 55 200 Anvil Shears- 95 62 160 Wire Rope Cutter


